Dog Pregnancy Calculator And Timeline
Pharmacies and gyms are always filled with tons and tons of human vitamins. With plenty of options, it’s logical to ask if some of these vitamins are needed for dogs too.
In reality, does your pet dog really need vitamins to stay healthy?
Most importantly, are there any hidden health risks linked to vitamins for dogs? What vitamins suit your dog?
For all your queries like these, here are the possible answers.
What Are Vitamins?
Vitamins are complex organic compounds that sustain life. In general, vitamins are readily present in our food.
Besides, pets like cats and dogs also require vitamins for overall growth and development.
Some of the popular vitamins both animals and humans require include –
- Vitamin A
- Vitamin C
- B vitamins (vitamin B-12, vitamin B-6, thiamine, riboflavin, pantothenic acid, niacin, folate, and biotin)
- Vitamin D
- Vitamin E
- Choline
- Vitamin K
Canines too need these vitamins, but they may require them in different quantities.
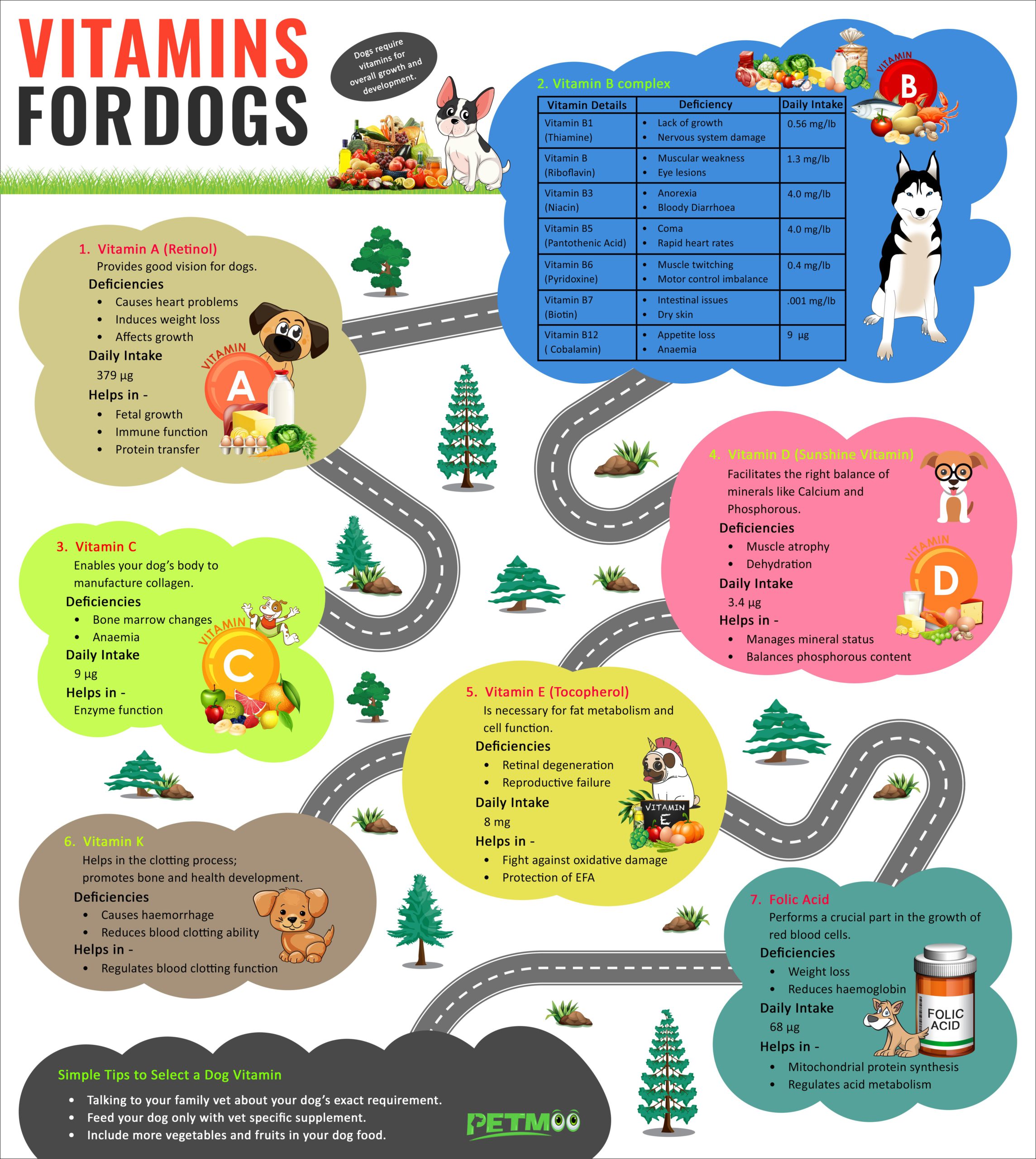
Vitamin A For Dogs
Vitamin A provides adequate vision for canines. Besides, vitamin A is a fat-soluble vitamin that manages cell function, immune function, fetal development, and overall growth.
Also called retinol, vitamin A plays a significant role in handling different biological processes, and promotes healthy vision
Vitamin A deficiency causes night blindness, skin problems, and joint problems.
Your dog requires around 2272 IU (International Units) of vitamin A for every pound of dry food. Also, the excess dose of this vitamin is about 50 times this range. Being fat-soluble, vitamin A excess can lead to toxicity issues.
B Vitamins For Dogs
Vitamin B1 For Dogs
Known as thiamine, vitamin B1 manages to support the nervous system and controls food and appetite stimulation metabolism. Your dog requires around 0.56 mg /lb daily to stay healthy.
Symptoms of Vitamin B1 deficiency in dogs include loss of appetite, bodily control defects, neurological problems, heart problems, and weakness.
Vitamin B2 For Dogs
Commonly known as riboflavin, vitamin B2 proves useful for healthy eyes and good vision. Also, riboflavin manages your dog’s cardiovascular function.
Moreover, this vitamin encourages your dog to manufacture niacin from tryptophan, the amino acid.
Symptoms of excess presence or deficiency of vitamin A include anorexia, eye lesions, flaking dermatitis, and muscular weakness
Your pet, in particular, needs not less than 1.3 mg of vitamin B2 daily.
Vitamin B3 For Dogs
Also known as niacin, this vitamin is vital for proper energy production, healthy nerves, and skin. Moreover, dogs that suffer from niacin deficiency may show signs of depleting appetite, bloody diarrhea, and inflamed gums.
In general, you should feed your dog 4 mg/lb of niacin every day.
Vitamin B5 For Dogs
Pantothenic acid or vitamin B5 regulates healthy skin, hormone production, and food metabolism. Besides, dogs prone to vitamin B5 deficiency can show signs of premature greying and may lose hair. Other signs include convulsions, bloody diarrhea, continuous salivation, anorexia, inflammation of the throat, cheeks, and lips
Ensure your dog is getting at least 4 mg of vitamin B5 daily.
Vitamin B6 For Dogs
Also known as pyridoxine, vitamin B6 enables the body to produce insulin, hemoglobin, and enough red blood cells. In short, vitamin B6 deficiency results in anemia in dogs, and some dogs are susceptible to skin lesions.
Dogs with vitamin B6 deficiency or excess presence may cause muscle weakness, impairment of balance and motor control, anemia in older dogs, muscle twitching, convulsions, and anorexia weight loss in puppies.
It’s recommended that you provide your dogs with 0.4 mg of pyridoxine or vitamin B6.
Vitamin B7 For Dogs
Called biotin, vitamin B7 facilitates digestion. Besides, this vitamin guides your body to break down proteins, fats, and carbohydrates.
Intestinal disruptions result due to vitamin B7 deficiency along with poor coat condition and dry skin.
You can feed your dog with 0.001 mg of vitamin B7.
B12 vitamins for dogs
At times, vitamin B12 is also called cobalamin. This vitamin also promotes the construction of RNA and DNA material, builds red blood cells, and manages the nervous system.
Vitamin B12 deficiency or excess intake causes bone marrow changes, anemia, lack of WBC, and appetite loss.
Typically, dogs require a minuscule amount of cobalamin (vitamin B12). They don’t need more than .00025 mg/lb daily.
Vitamin C For Dogs
In general, vitamin C manages cognitive aging. Also known as ascorbic acid, vitamin C enables your dog’s body to manufacture collagen, reduces inflammation, and fights harmful free radicals.
Collagen is a vital protein that secures the body’s ligaments, tendons, organs, muscles, and bones.
Dogs manufacture their ascorbic acid naturally.
Lack of correct amount of Vitamin D will lead to liver function changes, bleeding gums, muscle pain, joint weakness, bruises on the skin, and general weakness.
Vitamin D For Dogs
“The Sunshine vitamin” or vitamin D facilitates the right balance of minerals like calcium and phosphorous. Moreover, without sufficient vitamin D, your dog will find it challenging to maintain or develop healthy bones or muscles.
Also, vitamin D3 plays an essential part in securing calcium. Overall, vitamin D deficiency results in muscle atrophy, weak hair, dehydration, soft tissue calcification, weakness, and anorexia.
Vitamin K For Dogs
The dog’s body absorbs vitamin K via bacteria present in the intestine and different food sources. Importantly, vitamin K helps in the clotting process, and it also promotes bone and health development.
The main signs of vitamin K deficiency include altered clotting and blood hemorrhage.
Folic Acid For Dogs
Folic acid retains a crucial role in the growth of red blood cells, regulates nucleotide and amino acid metabolism, and guards cardiovascular health. Folic acid deficiency in dogs can cause anemia and weight loss.
Dogs need around 68 µg of folic acid daily.
Vitamin E For Dogs
Vitamin E defends the dog’s resistance against oxidative damage. This vitamin is essential for fat metabolism and cell function.
Vitamin E deficiency can cause muscle and eye degeneration and problems related to reproduction.
Your dog requires around 8 mg of vitamin E daily.
Choline For Dogs
Choline plays a prominent role in supporting the phospholipid cell membrane. Not to mention, choline promotes healthy liver and brain function and is regularly used to treat pets suffering from epilepsy.
Choline deficiency causes phospholipid cell membrane damage.
Do Dogs Require Vitamin Supplements Like Humans?
As you are already aware, your dog produces vitamins from his diet. Mostly, commercial dog foods that are labeled as balanced and complete are formulated to include all the vital nutrients, minerals, and vitamins your dog requires.
Food catered toward various life stages, including senior dog food, adult dog food, and puppy food, contain nutrients based on the dog’s age and need.
Large breed dog foods especially require these supplements as they are prone to stiffness and pain in the hip joints. Dogs that eat a regular balanced diet should not be fed additional vitamins unless instructed by your vet.
For dogs eating homemade food:
On the contrary, dogs eating homemade food may need extra supplements for overall growth and development.
However, these supplements should be matched with your dog’s diet, and merely feeding them will not produce the desired result.
Conclusion
At times, your vet may suggest including your dog’s food with vegetables and fruits and not vitamins. To sum up, vitamins form the core of dog health. Feeding a good quality dog diet is the only way to make sure your pet dog is absorbing all the essential vitamins.