Dog Pregnancy Calculator And Timeline
The Art of Understanding Your Pet’s Body Language
Of course, dogs are one of the most expressive and communicative animals. They express when they feel angry, fearful, nervous, sad, and happy. Moreover, they use their bodies and faces to communicate this information.
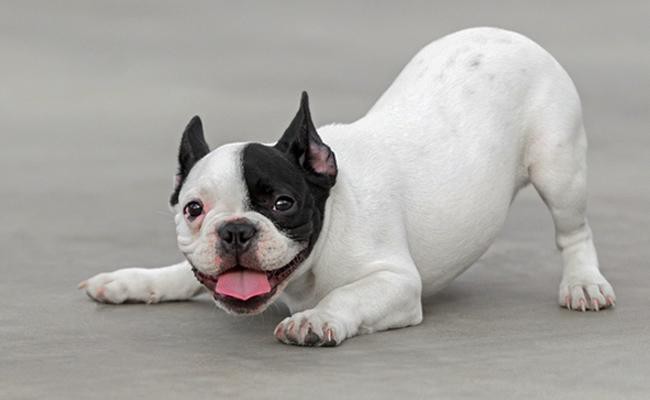
In general, dog body language encompasses a sophisticated and elaborate system of the nonverbal method of communication. Not to mention, dogs use overall demeanour, tail carriage, ear set, and facial expressions to express their feelings and intentions.
Therefore, to be fair, it’s simply not enough if you just focus your attention at just a single aspect of your pet’s body language.
Dog Faces
In general, different dogs have different face sizes and shapes, the basic facial expression of your dog can reveal a lot about his mental well-being.
1. The Eyes
In reality, your dog will, under control, change the size and shape of his eyes or the intensity and direction of his gaze.
Relaxed State of Mind
When your pet dog looks calm and relaxed, his eyes will appear in normal shape. Not to mention, some dogs feature almond-shaped eyes and others have round eyes.
Feared State of Mind
When dogs are feeling fearful, their eyes will look larger than normal. It means that your dog is feeling agitated in some way.
Showing Aggression
An aggressive dog also exhibits larger eyes much bigger than normal. In addition, if your dog shows smaller eyes, this also means he’s stressed or frightened. Additionally, dogs who are feeling unwell or in pain will often squint their eyes and dogs who grin may squint their eyes too.
The direction of the Gaze
In general, the way your dog looks also appears telling. Are you aware that dogs generally do not look into other’s eyes since they consider this behaviour threatening? If a dog looks at you displaying a relaxed facial gesture, shows friendliness and he expects you to notice him.
A dog directly staring at you indicates a tense situation, and it’s safe to look away. So, if a pet averts his gaze, it shows he is submissive. Furthermore, if your pet dog shows a large extent of the sclera or the white portion of his eyes, it can mean aggression.
Also called as “Whale Eye”, a dog shows this when he is, in fact, guarding a toy, or a chew bone.
2. The Mouth
Besides, drinking and eating, dogs perform a lot more activities with their mouths. However, they cannot talk like humans, the direction of their teeth, jaws, and lips speaks volumes.
In particular, when your pet dog is totally calm and relaxed, he will most probably keep his mouth slightly opened or closed. In certain cases, he may pant for breath, and this shows he’s cooling his body.
Feeling Frightened
A dog who’s submissive often keeps his mouth closed. In addition, he might also slightly pull back his lips at the corners. Moreover, when your dog feels uptight, he may yawn in an animated fashion.
Submissive Look
When dogs feel submissive, they move their lips vertically and show their incisors and canines. Especially, this gesture is followed by squinty eyes, lowered head, whining or yelping.
Aggressive look
A dog who’s ready to display aggression will move his lips and expose his teeth. In addition, some dogs also pull their lips upwards and at the same time wrinkle his muzzle.
So, when you see a dog showing this signal, never cross his path and simply walk away.
Biting dog body language
Once a dog gets ready to taste some flesh, he will pull his lips not only up but also back. Overall, he will expose his teeth before plunging to take the bite. Additionally, dogs show an “aggressive pucker.”
In this posture, they will display their puffy lips and also expose their wrinkled forehead.
Dog Tails
Most people assume that when a dog wag’s his tail, he is happy.
However, there are various reasons for your dog’s tail wagging behaviour
- A dog will wag it’s tail when it feels aggressive.
- Notably, a dog’s capacity to communicate with his tail actually depends on the variety of tail.
- Most dogs feature “natural tail.”
Relaxed tail wagging
When your dog appears calm and happy, he will display his tail in its original position. Also, he will wag it sidewards. If it feels submissive or nervous, he will keep his tail lower and at times he will tuck it in between his rear legs.
When your dog is scared
If he feels extremely submissive or scared, he will place his tail tightly against his belly.
Feeling alert
Your dog will hold its tail at a much higher position than normal when he feels aroused. In fact, he will hold his tail as stiff as possible.
Dog Ears
Each and every dog have a different type of ears. In particular, the shape and size of your pet dog’s ears will decide how well he communicates with these ears.
Not to miss, the ASPCA supports dog parents and breeders to keep their pets with their birth look. However, they do not condone nor favour ear cropping.
Many dog owners prefer cosmetic ear cropping and as a result, this causes dogs discomfort and unnecessary pain.
- Relaxed appearance – Your dog will hold his ears in a natural posture when he feels comfortable and relaxed.
- Alert posture – An alert dog will raise his ears and move them in the direction of action. At the same time, a dog may also raise his ears when he feels aggressive.
- Friendly posture – When your dog pulls his ears back, he wishes to communicate that he is friendly.
- Feeling submissive – If your dog’s ears are stuck out, it means he’s feeling submissive or frightened.
Dog Hair
Although dogs seldom communicate with their hair, you can still grasp some things from a dog’s coat or hair. First and foremost, a stressed or a scared dog is more susceptible to shed extra hair than normal.
Next, dogs use a method called “piloerection” which is also called as “raising the shackles”. They can raise their hair along their spine. Therefore, a raised hackles convey that a dog feels excited, nervous, unsure, insecure, angry, or afraid of something.
General Body Posture
Dogs use their bodies in a subtle manner to express their intentions. So, they attempt to appear larger, smaller, or normal. If your dog’s looking contented or safe, he will put up a normal look- weight evenly balanced and relaxed muscles.
He may also run wild or bounce around with animated movements, but his muscles and facial reaction will appear calm.
Scared
A dog might hunch and try to appear small when he feels scared. At times, some dogs will cower or lower his body. He will keep his head low. However, if your dog is afraid of something, he will move away from it.
For example, if a dog feels scared, he will most probably move towards you. On the other hand, when a dog looks curious or uncertain, he will keep his weight-balanced over his rear since it’s easy for him to back off if he feels so.
Submissive dog body language
A submissive dog appears quite similar to a dog under fear because he projects himself small. In addition, he may even cower or lower his body.
Assertive dog body language
A dominant dog projects himself large. He will stand on his tiptoes and his body weight will be evenly distributed.
Summary - The Complete Body Language
The messages dogs send using their body can appear very subtle. It’s important to know whether your dog is angry, upset, insecure, or scared.
- Contented, Happy – When your pet looks happy, he will appear relaxed. His facial gesture is neutral and his mouth corners might be slightly positioned tightly as though he’s giggling.
- Excited – His body language will be playful. He looks ready for action. In addition, he appears natural and tail and ears are held high. In fact, excited dogs often keep their mouths open, and they may also bark.
- Alert – When he looks alert, he appears focused and intense. He positions are body upright and all his weight are balanced on all fours. He keeps his mouth closed.
- Playful – He exhibits bouncy and jerky body movements. He may also move around in animated leaps, turns, and twists. Also, your dog might take off encouraging a chase, paw at you, and dodge at you.
- Aroused – When he feels aroused, it becomes quite difficult to distinguish it from being excited or alert. However, an aroused dog always keeps his hackles up. Moreover, he may look directly at a person. In general, a dog can feel aroused by an odour or a sound we can’t recognize.
- Submissive – During active submission, a dog will make his body appear small by getting low or hunching over to the ground. He keeps his wag tucked or low, at times wagging it briskly.
In particular, he places his neck near the ground but keeps his muzzle pointing upwards towards the individual. Besides, some dogs, in fact, puppies urinate. - Dominant – During the interaction, dogs convey an assertive, confident attitude that’s known as “dominant.” If he feels dominant, he will stand tall and shows signs of being tense. He holds his ears forward and keeps his tail rigid and high. In other words, he will maintain direct eye contact.
- Scared, Fearful – When your dog feels scared, he keeps his body hunched. If he plans to escape, he will keep all the body weight over his rear. The muscles all over his face might appear rigid and tense.
- Defensively aggressive – People refer to these type of dogs as putting up “a good offence”. Generally speaking, it depends on how close your pet is to the danger.
- Fearfully aggressive – Some dogs never push to aggression, but other dogs will try if they feel cornered. Suppose, if he bites or snaps, it’s super fast, and then he moves away as far as possible from the threat.
What Does Your Feline’s (Cat) Body Language Suggest?
What is your feline friend thinking? Watch closely, your pet cat’s body language might give it away. In general, cats convey a different type of signals. It includes vocalizations, facial expressions, and body postures.
Therefore, by understanding how to read these feline signals, you can prevent potential aggression and misunderstandings. However, but for many, cat body language sounds Greek and Latin, difficult to understand.
So, animals experts guide us to understand kitty’s vocalizations and cues.
1. Classic Halloween Pose
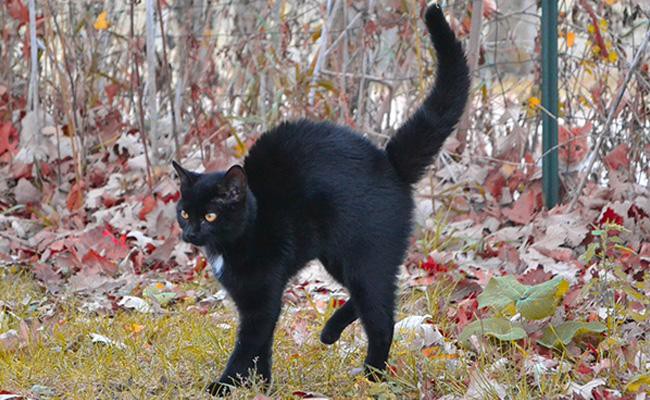

The best way to understand a cat’s mood rest with its tail. When a cat keeps it high, it indicates confidence. Moreover, when it curls around another person’s legs, it indicates friendliness.
Besides, when its tail is tucked between the legs, it shows anxiousness. In general, the upright bottle posture means that your cat feels threatened.
Overall, when combined with unsheathed claws, and the arched back, the posture indicates you should move back.
2. The Affectionate Blink
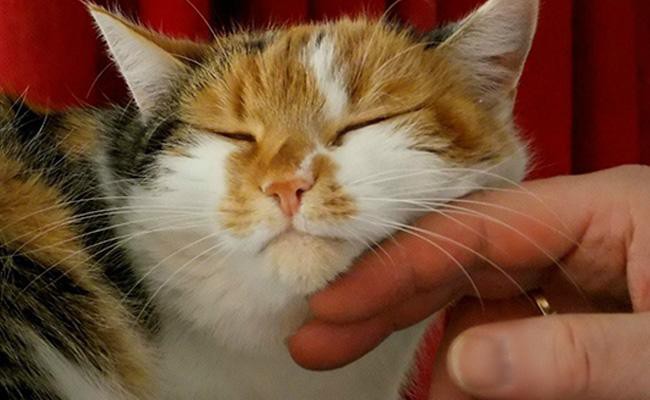

If a cat welcomes another person or a cat with a relaxed blink, it reflects affection. The reason. Generally, in the cat world, closing eyes in front of another feline shows trust.
Finally, by blinking slowly, you are signalling that you are comfortable with this gesture and show no danger.
3. Tummy Show
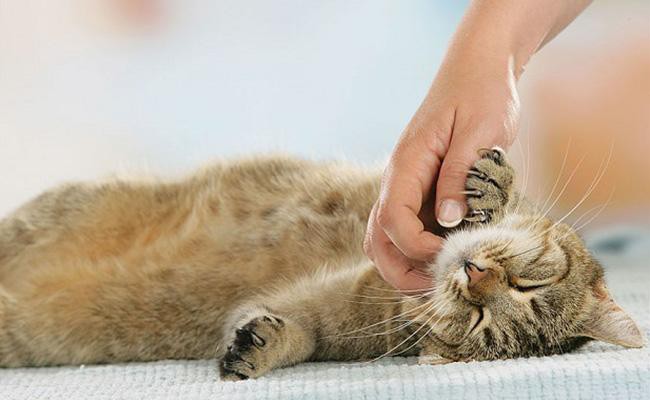

In fact, when your cat looks relaxed and content, she may roll over and stretch out. But, in certain situations, when it feels sidelined, followed by sharp teeth and extended claws, reflects defensive tactics.
Overall, with other cat-human interactions, it’s necessary to understand what your cat loves.
4. Audio signals
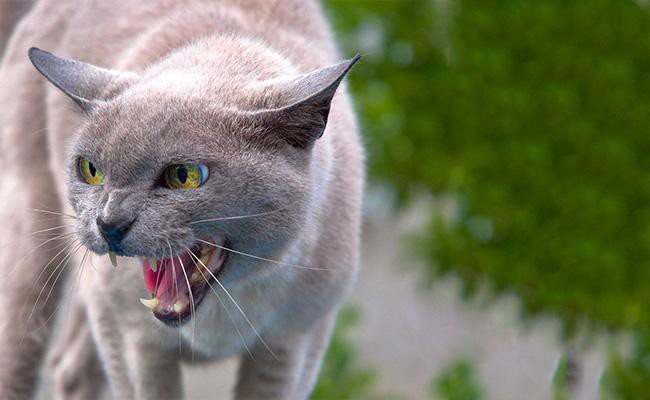

As a responsible cat owner, you better learn the intricacies of your cat’s body language so you can differentiate between an emergency call and a request for food. For example-
- Caterwauling sounds are made by cats when it feels threatened or scared by other cats. In addition, this vocalization is very popular amongst deaf cats.
- Spitting, hissing, and growling are immediate warnings to stay away.
- High-frequency chatting and gurgling show affection.
- Purring can also indicate a very cool behaviour and at times it also means contentment.
5. Leave Me Alone
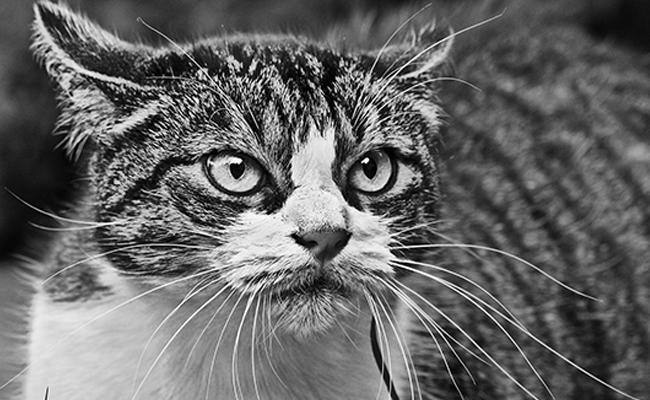

Are you aware that cats are impetus-driven carnivores by nature? So, when a cat sees something moving, they are programmed to chase it. Closer and closer, these animals move inch by inch forward, and then they suddenly pounce and kill.
Suppose, if the victim happens to be you, then the best response is to freeze. This sudden stop-action can interrupt the feline’s stalking pattern.
The set of tell-tale warning signals include
- Flattened ears
- Low twitching tail
- Dilated pupils
When you witness these signs, just back off and leave your cat alone.
6. The direct stare
In reality, a cat will move towards a person who is avoiding direct eye contact. In fearful situations, the cat’s pupils expand expressing anguish. Also, when dilated, the cat’s eye absorb as much information as possible.
An angry cat will constrict its pupils. Furthermore, they also react to ambient lighting.
The Bottomline
So, its imperative that you learn your cat’s body language for a better understanding.